3 Ways to Manage Freelancers and Independent Contractors (Guide)

Overview
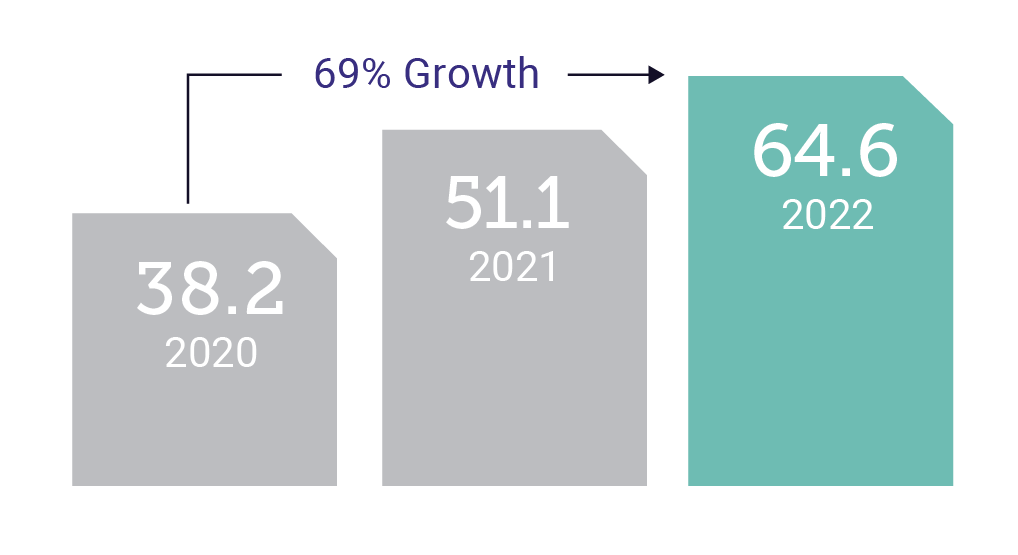
Total Number of Independents (in millions)
The demand for independent professional talent is continuing to grow year over year—64.4 million Americans work independently according to our latest research—and businesses are pushing full steam ahead seeking the best ways to find, engage, and retain maintain relationships with these professionals.
As they seek the many benefits of this talent pool, enterprises must also evaluate their contingent workforce management programs holistically to ensure they are truly meeting their core objectives: reducing enterprise manager time, streamlining processes, minimizing misclassification risk, lowering costs, and ensuring independent contractor satisfaction.
GATE
But not all independent contractor engagement practices—new or legacy—are created equal. Some businesses, in fact, are pursuing or clinging to independent contractor initiatives that increase the risk of misclassification or alienate strategic independent talent. It is critical that business leaders pursue engagement solutions that, in addition to mitigating independent contractor-related risks, also improve program adoption, visibility, and independent talent re-engagement. Independent workers range from highly-established professional services providers to more commoditized temporary workers. As shown in Figure 1 below, they often range significantly in terms of their compliance status.
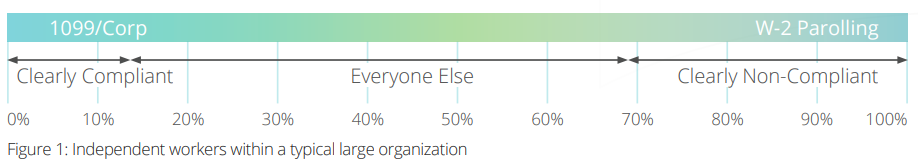
Figure 1 shows the spectrum across which the typical independent worker may comply with federal and state rules for worker classification.
In this guide, you will learn
3 Ways independent workers are defined
Independent workers are typicall defined in three ways:
1. CLEARLY COMPLIANT WORKERS:
Enterprises can engage the leftmost group of workers, who are clearly compliant, on a 1099 basis with little risk of reclassification.
2. CLEARLY NON-COMPLIANT WORKERS:
Workers on the rightmost side of the spectrum are clearly non-compliant. These workers do not see themselves as a true independent business and are generally happy to engage through a traditional payrolling program that provides them with standard W-2 employment status and a regular paycheck.
3. GRAY ZONE WORKERS:
The compliance status for gray zone workers, the workers who fall in the middle of the spectrum above, may not be easily discernible without further analysis. These workers often see themselves as independent professionals and are unwilling to engage through payrolling programs. It is this gray zone of independent workers that represents the majority of reclassification risk—and is the primary target of compliance and engagement programs.
1. Rogue Engagement Approach
Many businesses today fail to establish engagement policies for independent workers, resulting in the arrangement depicted in Figure 2. In this approach, or lack thereof, independent contractor engagement is typically decentralized across the enterprise and largely managed by the same enterprise managers who are requesting the talent.
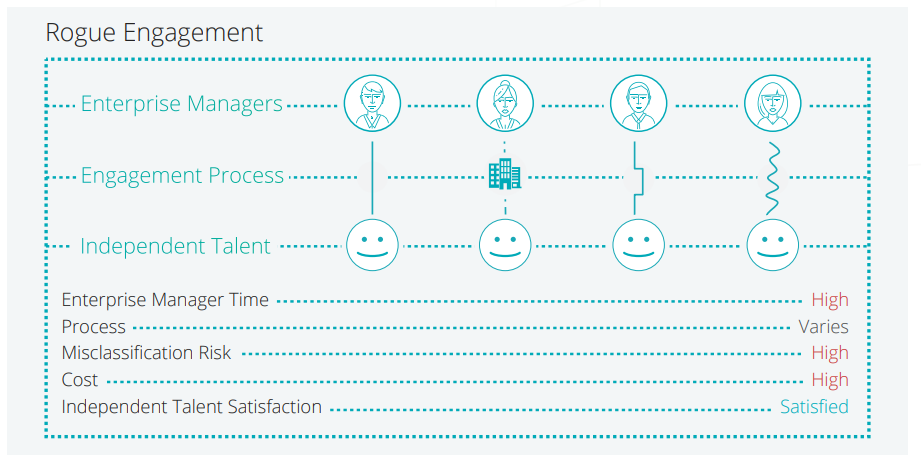
Failing to have a program for engagement and risk mitigation results in high misclassification risk, high cost, and inefficient use of enterprise manager time.
| ENTERPRISE MANAGER TIME In rogue engagement, the enterprise manager works with the independent contractor to create a Statement of Work and get them set up for payment, but the engagement process may vary from manager to manager. This results in a longer time-to-productivity and more work on behalf of the manager. |
|
 |
PROCESS As a result of a highly discretionary process, rogue engagement leads to inefficiencies and opens the enterprise up to significant risk from misclassification. |
 |
MISCLASSIFICATION RISK In most cases, the manager is not fully appraised of the risks of misclassification and treats every worker as a 1099, resulting in a high risk of misclassification. |
 |
INDEPENDENT CONTRACTOR SATISFACTION In rogue engagement, independent contractors are generally satisfied, as they have direct access to the enterprise manager and can complete their project with little interference from corporate procedures and policies. |
 |
COST As rogue engagement programs are not centrally managed, the enterprise misses out on the opportunity to strategically manage this spend as a category and reap the benefits of continual process and program improvement. Costs are high, simply because they are not actively managed. |
In this approach, enterprises engage a large percentage of their independent workforce—including many potentially non-compliant workers as “qualified” 1099s. Often, enterprises feel this engagement decision is justified because the workers are self-incorporated, have their own websites, have employees, or have worked as independent contractors in the past. These qualifiers, however, have little bearing on true regulatory criteria for independent contractor compliance. Consequently, this approach does little to reduce an organization’s risk profile.
2. Restrictive Engagement Approach
Another common approach is to establish independent contractor engagement policies that force most, if not all, gray zone independents into a traditional payrolling program. This is depicted in Figure 3. In a restrictive engagement approach, the enterprise seeks to centrally manage their independent contractor engagement program, either in-house or through a traditional third-party compliance provider.
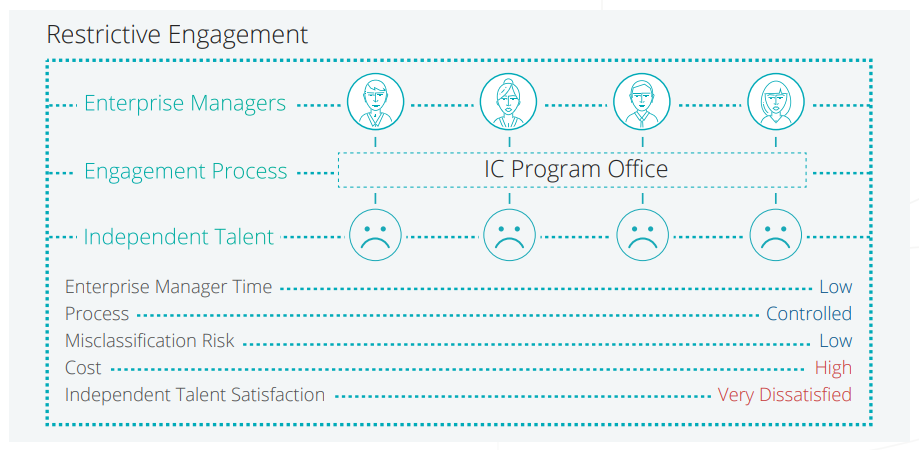
Restrictive engagement programs often alienate a huge percentage of the independent workforce and lead to even greater talent loss.
| ENTERPRISE MANAGER TIME Restrictive engagement programs typically leverage a standard workflow, involving a referral process on behalf of managers, which does not require a lot of dedicated time on their part. |
|
 |
PROCESS The enterprise manager will generally refer workers directly to the program office to evaluate compliance risk. If the worker does not meet all of the tests and requirements to operate as a 1099, they revert to a W-2 payroll program. This process is more efficient than the rogue engagement approach, bringing spend under management and reducing the risks of misclassification. |
 |
MISCLASSIFICATION RISK One benefit of restrictive engagement is that misclassification risks are low due to the fact that workers are directed into either a 1099 or payroll program depending on whether or not they meet specified requirements. |
 |
COST Cost for restrictive engagement programs is high due to the markup of payroll programs which range between 20 to 40 percent. |
 |
INDEPENDENT CONTRACTOR SATISFACTION Restrictive engagement programs lead to a high level of dissatisfaction for self-employable talent who see themselves operating as an independent contractor, but may not check every box to qualify. When these professionals are forced on a traditional payroll program, they find frustration in the inability to bill on milestones or take advantage of any of the associated tax benefits of working as independent professional. |
This approach highlights the common outcome of such payroll-centric compliance programs: a crisis of adoption. Higher-billing workers frequently become averse to these programs and seek out ways to circumvent them or leave their assignments early. Meanwhile, their managers are similarly motivated to sidestep these programs because they are focused on keeping their independent workers happy, even if that means defying corporate engagement policies.
The end result? Program acceptance suffers, adoption declines, talent flees, rogue engagements proliferate, reclassification risk lingers, and true spend visibility becomes impossible to achieve.
3. Preferred Engagement Approach
An effective independent contractor compliance and engagement program must achieve two key objectives: mitigating independent contractor risk and ensuring program adoption by both managers and talent. The support and offerings required by higher-billing, professional independent contractors are typically vastly different from those required by lower-end administrative workers.
Higher end independent talent value programs which help them setup their own legal structure, provide access to insurance, administer back office functions on their behalf, and give them exposure to further contract opportunities. To successfully and compliantly engage this talent pool, organizations should consider a flexible, consultative solution.
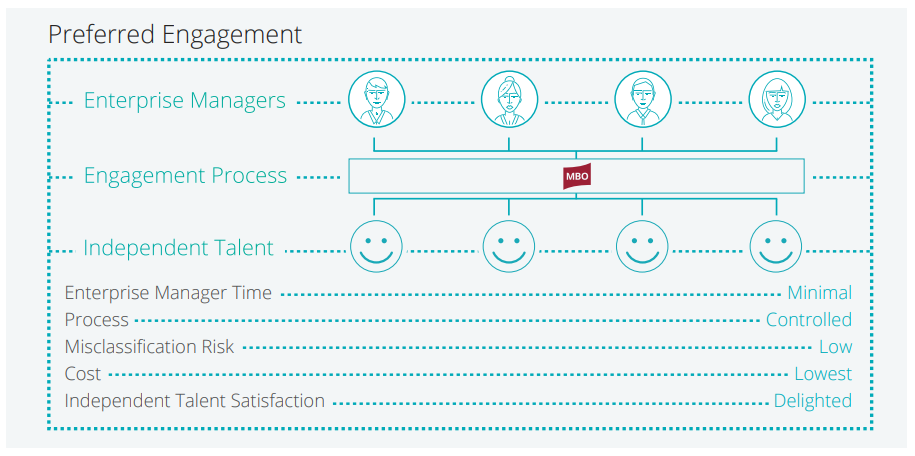
Preferred engagement programs provide workers with multiple engagement options, giving them more choice and providing more value in their relationship with their enterprise client.
The preferred approach not only offers enterprises greater scale, efficiency, and improved category management, but also seeks to meet the independent talent “where they are” in their journey to become a fully qualified 1099. This approach both reduces risk and provides all a more talent-friendly approach to engagement. In the preferred approach, the worker is provided with more than two engagement options (as depicted in Figure 4), giving them more choice and providing more value in their relationship with their enterprise client.
| ENTERPRISE MANAGER TIME In the preferred approach, enterprise manager time is kept to a minimum as qualified independent professionals are referred directly to an enrollment site that facilitates worker qualification and onboarding. |
|
 |
PROCESS The process for the preferred approach is very controlled, thanks to the use of technology that streamlines and simplifies many time-consuming processes. A successful independent contractor engagement program encompasses the processes and technology to find, source, engage, pay, and manage independent workers. By combining a direct sourcing strategy—identifying candidates for available opportunities using internal resources rather than third-party intermediaries—with technology such as a talent marketplace, organizations can simplify the sourcing, engagement, and re-engagement processes. |
 |
MISCLASSIFICATION RISK A preferred program recognizes that workers each have different levels of self-employability, as well as individual needs and requirements. Offering flexible and varying engagement options keeps misclassification risk low and helps attract and retain top talent. |
 |
COST This approach provides a significant cost-savings opportunity for the enterprise as they avoid costly payroll mark-ups, which range from 20-40%. Enterprises also gain an immediate cost benefit from avoiding fines and penalties associated with independent contractor reclassification, including IRS follow-on audits as well as audits by other federal or state agencies.Down the road, widespread program adoption enables enterprises to realize significant improvements in their visibility into contractor-related spend. Organizations will have a platform upon which they can more easily review enterprise-wide expenditures and control costs by managing rates, supervising budget adherence, and only engaging contractors whose rates are within established benchmarks. |
 |
INDEPENDENT CONTRACTOR SATISFACTION This talent-centered approach provides products and services which afford independent professionals the opportunity to recognize many of the benefits of working as an independent contractor. For example, in a preferred engagement approach, independent contractors can easily take advantage of tax savings by establishing a pass-through business entity, gain access to tax-advantaged benefits including a retirement plan and Health Savings Account (HSA), and receive support from specialists who can support them in maintaining a compliant business, provide assistance with quarterly tax estimate requirements, and guide them through their client’s onboarding process so they can start work quickly and compliantly. |
Additional thoughts
Independent contractors bring many benefits to today’s organizations—on-demand expertise, financial savings, and staffing flexibility. As use of this workforce continues to grow, companies must put policies and procedures in place for proper classification, engagement, and management of these workers, especially when bringing higher-billing talent on board.
Looking to expand how you engage independent talent?
Related Posts
Trending
Subscribe to our blog
Get a weekly email of our latest posts sent straight to your inbox
Learn more about the MBO Platform
FOR INDEPENDENT
PROFESSIONALS
Start, run, and grow
your independent business with MBO
FOR
ENTERPRISES
Engage, scale, and optimize
your independent workforce


